- SERVICES
- RESEARCH AREAS
- AAV Services
- Agriculture and Food Science
- Antibody Discovery & Immunology
- Biomarkers
- Cancer Research
- Infectious Disease
- Synthetic Biology
- Metagenomics
- Genome Editing and Engineering
- RESOURCES
- Sample Submission Guidelines
- FAQs
- Free Universal Primers
- Educational Resources
- Citations & Publications
- NGS Platforms
- Global Network Services
- Sample Submission Guidelines
- PRODUCTS
- Tubes
- Sealing Films and Foils
- Microplates
- Instruments
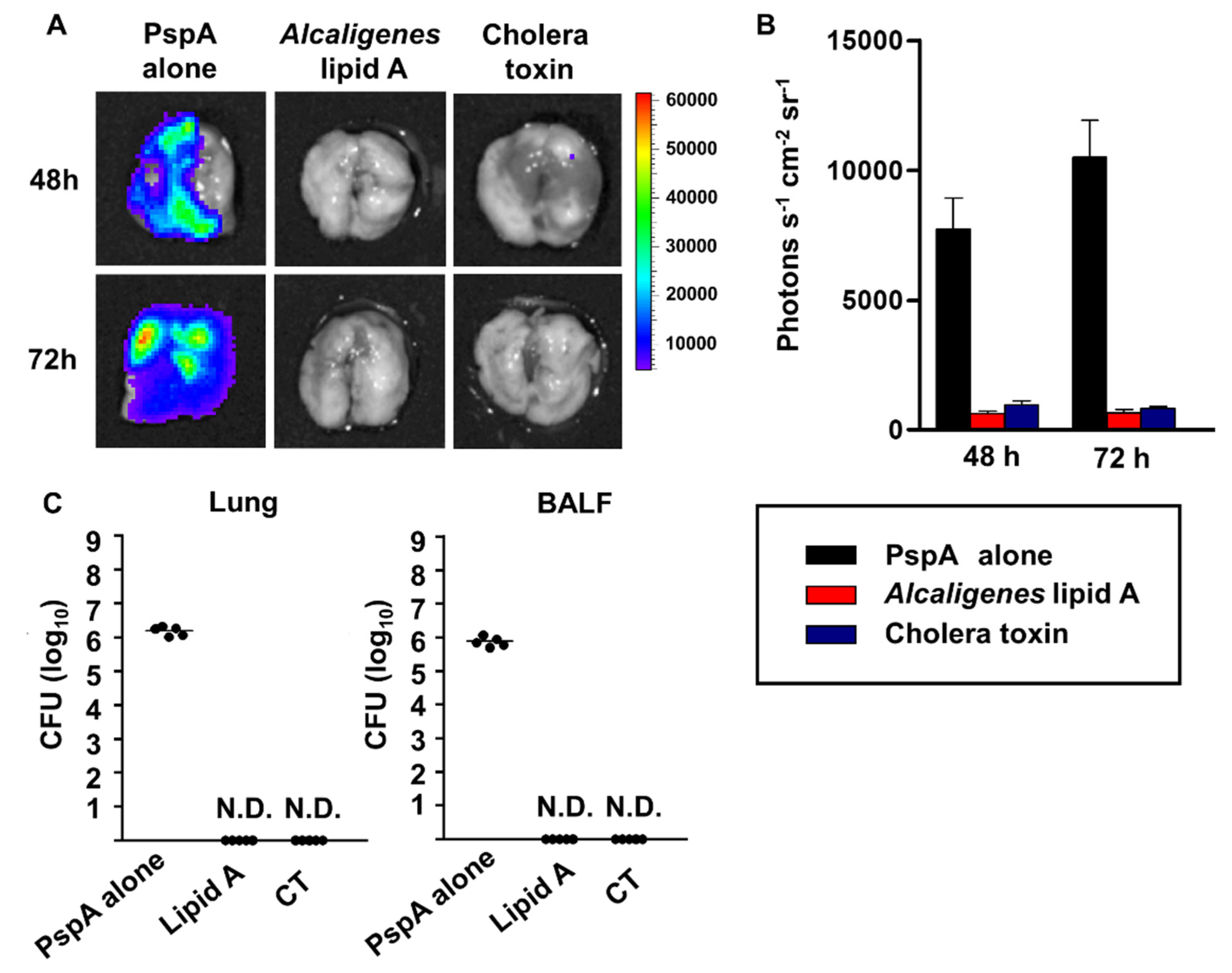
- WHO: RdRP and E gene
- China CDC: ORF1ab and Nucleoprotein N
- US CDC: N gene
- Genomic DNA Purification
- DNA Fragment Purification
- Exosome Related
- RNA Purification
- Direct PCR
- PCR Related
- Restriction Enzymes
- DNA Markers
- Related Products
- Prestained Protein Markers
- Agarose
- Lentivirus Related
- Mycoplasma Detection
- COMPANY
- About GENEWIZ
- About Brooks
- News and Events
- Careers
- Locations and Hours
- Contact Us
- LEGAL
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Imprint

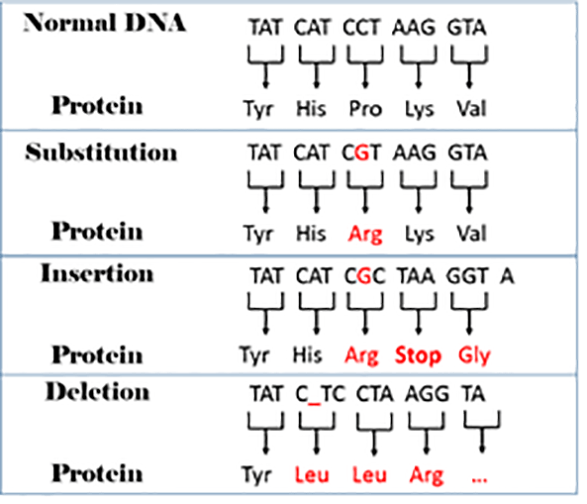

5 Nasal Mutation Practice Sindarin Lessons Worksheets
To start the lesson, I invite the mutation experts from the day before (How Does Evolution Happen? Autodesk autocad 2015 tutorialengineering design specialist. ) to remind us what a mutation is, and how mutations can be a driving factor in evolution. Instead of asking just one student from the expert pool, I ask the mutation experts to stand, and state one fact they know about mutations and their role in. Lesson 4: Mutations What causes albinism? This rare albino alligator must have the specific 'instructions,' or DNA, to have this quality. The cause of albinism is a mutation in a gene for melanin, a protein found in skin and eyes. Such a mutation may result in no melanin production at all or a significant decline in the amount of melanin. Mendelian genetics. Video transcript. World photos american meadows equestrian center. Voiceover: So, today we're going to talk about the different types of genetic mutations that you would find in a cell. But first, I want to review the central dogma of molecular biology and how the genetic information of a cell is stored in the form of DNA, which is then transcribed to form RNA.
